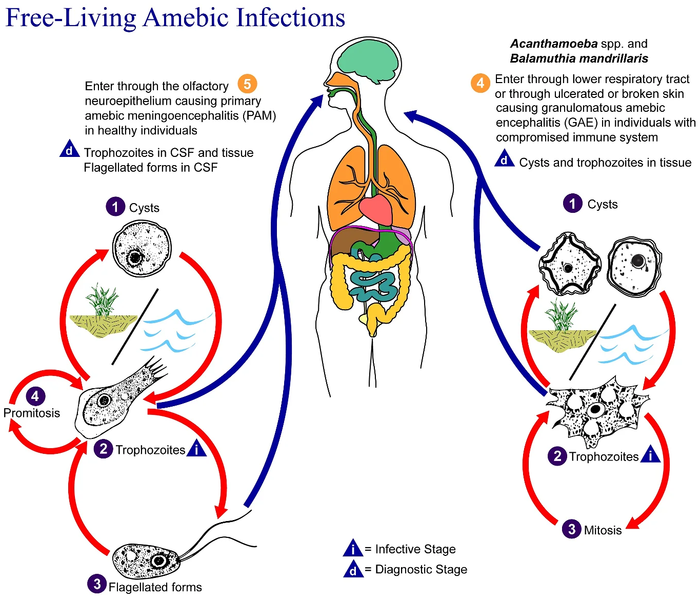
Ficheiro:Free-living amebic infections.png
Tamaño desta vista previa: 700 × 600 píxeles. Outras resolucións: 280 × 240 píxeles | 560 × 480 píxeles | 896 × 768 píxeles | 1.195 × 1.024 píxeles | 1.365 × 1.170 píxeles.
Ficheiro orixinal (1.365 × 1.170 píxeles; tamaño do ficheiro: 715 kB; tipo MIME: image/png)
Historial do ficheiro
Prema nunha data/hora para ver o ficheiro tal e como estaba nese momento.
| Data/Hora | Miniatura | Dimensións | Usuario | Comentario | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actual | 2 de febreiro de 2023 ás 09:24 |  | 1.365 × 1.170 (715 kB) | Materialscientist | https://answersingenesis.org/biology/microbiology/the-genesis-of-brain-eating-amoeba/ |
| 20 de xullo de 2008 ás 06:30 |  | 518 × 435 (31 kB) | Optigan13 | {{Information |Description={{en|This is an illustration of the life cycle of the parasitic agents responsible for causing “free-living” amebic infections. For a complete description of the life cycle of these parasites, select the link below the image |
Uso do ficheiro
As seguintes 2 páxinas usan este ficheiro:
Uso global do ficheiro
Os seguintes wikis empregan esta imaxe:
- Uso en de.wikibooks.org
- Uso en en.wiktionary.org
- Uso en fi.wikipedia.org
- Uso en fr.wikipedia.org
- Uso en hr.wikipedia.org
- Uso en is.wikipedia.org
- Uso en it.wikipedia.org
- Uso en pl.wikipedia.org
- Uso en te.wikipedia.org
- Uso en vi.wikipedia.org
- Uso en www.wikidata.org
- Uso en zh.wikipedia.org